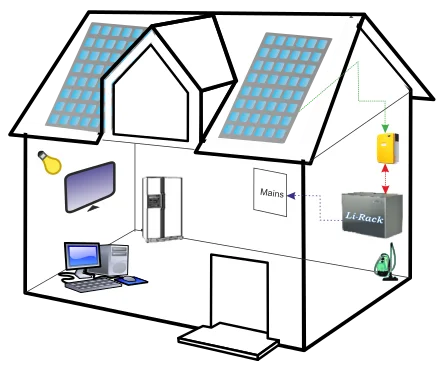
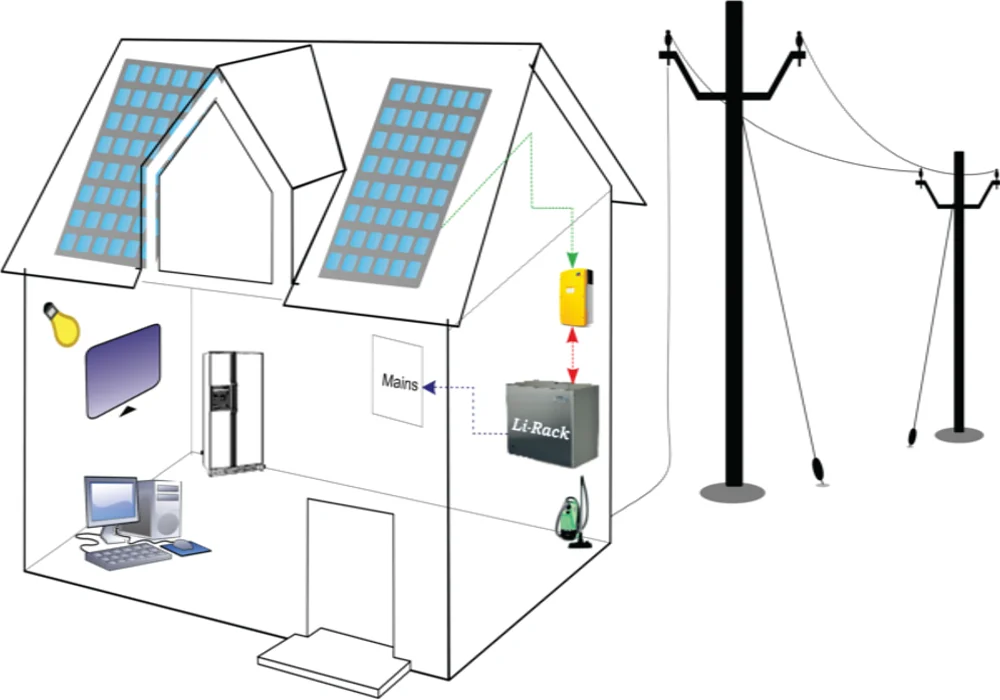
Renewable energy is on the rise. Renewable energy is energy derived from natural sources that is replenished more quickly than it is consumed. Sunlight and wind, for example, are constantly replenished sources. Renewable energy sources abound and are all around us. In comparison, fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas are non-renewable resources that take hundreds of millions of years to form. When fossil fuels are burned to generate energy, they emit harmful greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide. Innovation reduces costs and begins to deliver on its promise of a clean future. Solar and wind power generation in India is breaking records and being integrated into the national power grid without compromising its reliability.

THE MOST POPULAR
RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES
-
SOLAR ENERGY
Solar energy is one of the most abundant forms of clean, renewable energy because it harnesses the sun's energy. Solar technologies have the potential to provide heat, cooling, natural lighting, electricity, and fuel for a wide range of applications. Solar technologies use photovoltaic panels and mirrors to concentrate solar radiation and convert sunlight into electricity. The amount of solar radiation, also known as insolation that reaches the Earth's surface every hour is greater than all of the energy currently consumed by human activities.

Solar energy generation has a number of advantages, including the long-term availability of renewable energy sources and improved energy efficiency. Solar energy has the potential to reduce pollution and the use of nonrenewable energy sources while also significantly lowering power costs. Vision Mechatronics is dedicated to transforming the world's energy supply into 100% renewable energy.
-
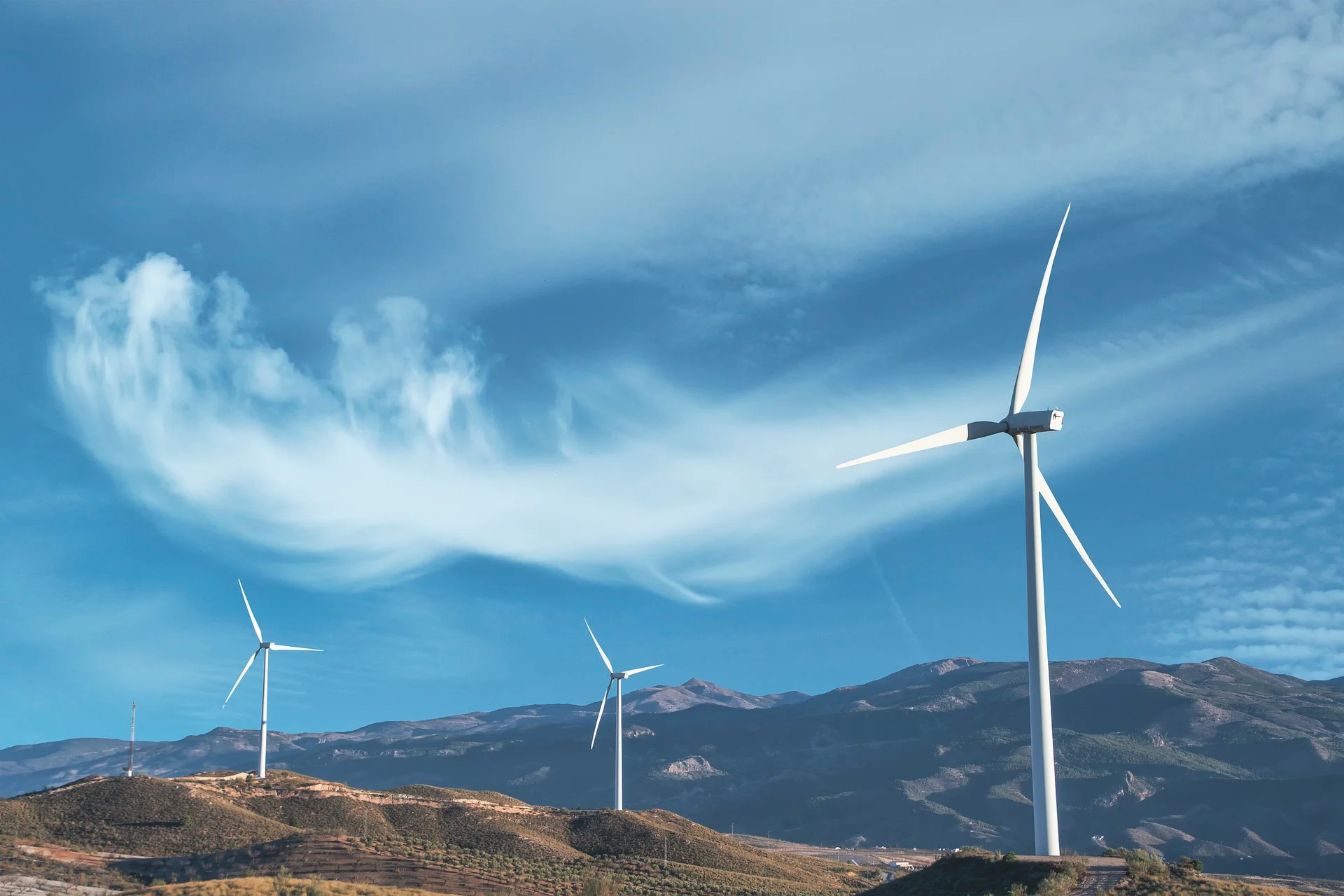
WIND ENERGY
Wind energy production has grown dramatically since the first turbines were developed in the late 1800s. Today, turbines are as tall as skyscrapers, with turbines nearly as wide in diameter. They stand at attention around the world. Wind energy turns a turbine’s blades, which feed an electric generator and produce electricity.
The world's technical potential for wind energy exceeds global electricity production, and ample potential exists in most regions of the world to enable significant wind energy deployment from offshore wind power. Land-based, utility-scale wind turbines provide one of the lowest-priced energy sources available today. Not only is wind power abundant and inexhaustible, but it also provides electricity without burning any fuel or polluting the air, which helps reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.

-
HYDRO ENERGY
Hydropower is the ability to generate energy using the flow of water to turn generators. It relies on generally stable rainfall patterns. It harnesses the energy of water moving from higher to lower elevations. Although it can be generated using reservoirs and rivers, its reservoirs often have multiple uses. Some examples are drinking water, water for irrigation, flood and drought control, navigation services, and energy supply.
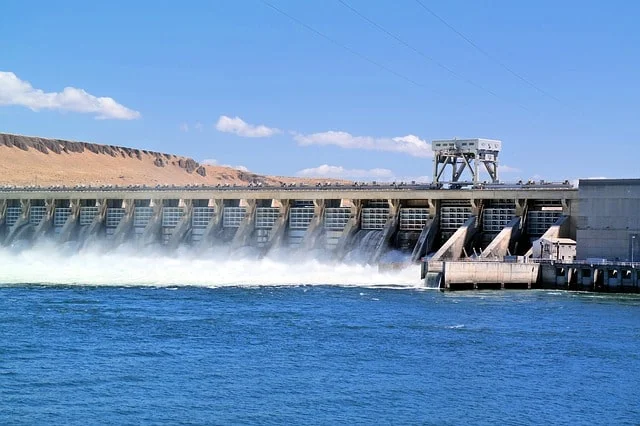

Large hydroelectric plants, or mega-dams, are often considered a nonrenewable source of energy, in large part because they can have a negative impact on the environment. Mega-dams divert and reduce natural flows, restricting access for animal and human populations that rely on those rivers. Small hydroelectric plants (with an installed capacity below about 40 megawatts), when carefully managed, do not tend to cause as much environmental damage, as they divert only a fraction of the flow.
-
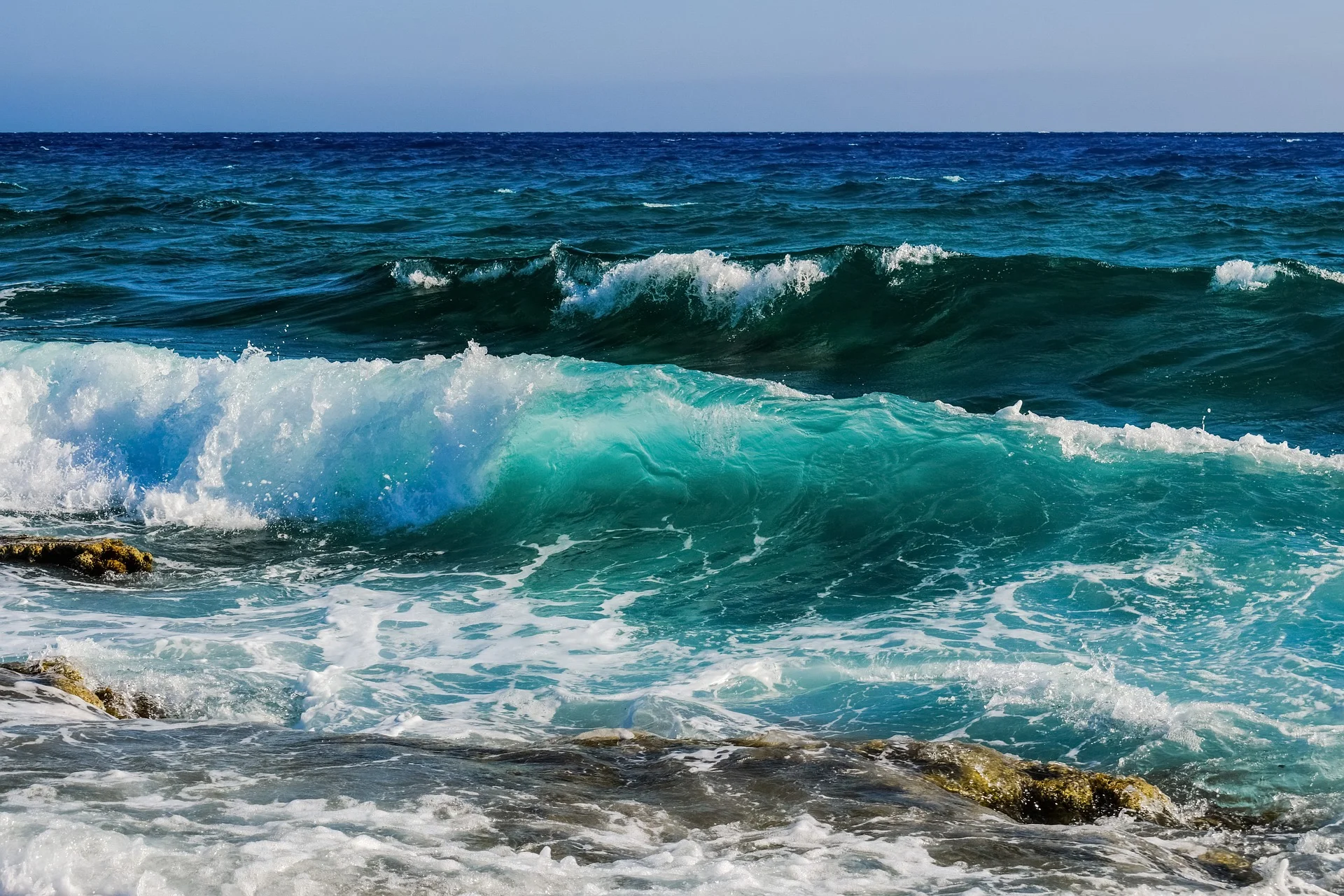
OCEAN ENERGY
Green energy is energy that is extracted, generated, and consumed without releasing harmful chemicals or greenhouse gases into the air. Ocean energy is a renewable energy source that derives from technologies that use the kinetic and thermal energy of seawater - waves or currents, for instance - to produce electricity or heat.
Ocean energy and wave energy are still in the developmental phase, but the ocean will always be ruled by the moon’s gravity, which makes harnessing its power an attractive option. Some tidal energy approaches may harm wildlife, such as tidal barrages, which work much like dams and are located in an ocean bay or lagoon. Like tidal power, wave power relies on dam-like structures or ocean floor–anchored devices on or just below the water’s surface.

-
BIOMASS ENERGY
Bioenergy is the conversion of solid fuel made from plant materials into electricity. Biomass is organic material that comes from plants and animals and includes crops, waste wood, and trees. When biomass is burned, the chemical energy is released as heat and can be used to generate electricity with a steam turbine. Although biomass involves burning organic materials to produce electricity, nowadays this is a much cleaner, more energy-efficient process. By converting agricultural, industrial, and domestic waste into solid, liquid, and gaseous fuel, biomass generates power at a much lower cost.
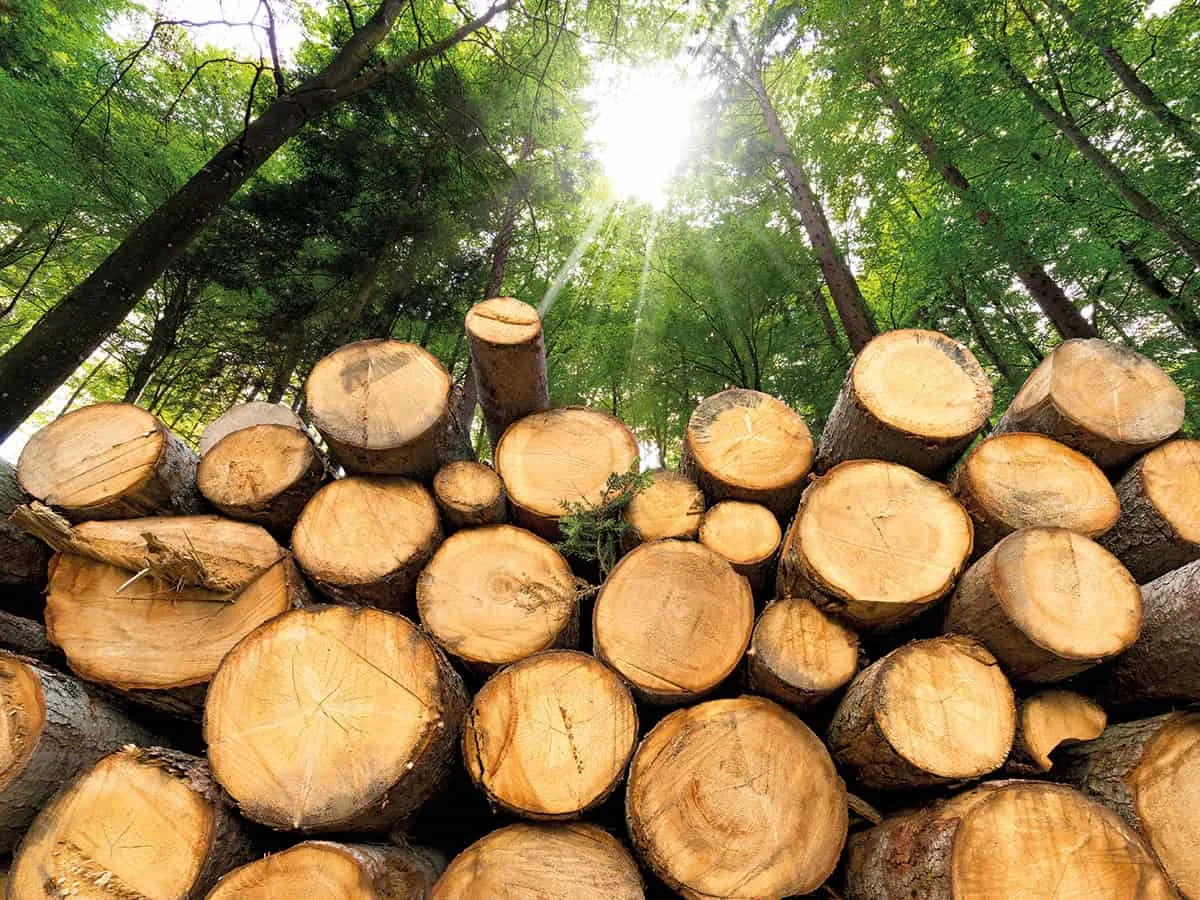

However, there are many forms of biomass that produce higher carbon emissions than fossil fuels. There are also negative consequences for biodiversity. Still, some forms of biomass energy could serve as a low-carbon option under the right circumstances. For example, sawdust and chips from sawmills that would otherwise quickly decompose and release carbon can be a low-carbon energy source.
-
GEOTHERMAL ENERGY
Geothermal is energy powered by the earth. Geothermal energy harnesses thermal energy from the earth's interior. Geothermal energy is one of the oldest forms of renewable energy that we know of. It has been used by humans for centuries to heat homes and produce electricity. The earth's core is extremely hot, due to the slow decay of radioactive particles in rocks. This heat is transferred to underground water, which can be accessed through deep wells. The hot water is then pumped through a turbine to create electricity.
Geothermal plants typically have low emissions, as the steam and water used are recycled back into the reservoir. In some cases, geothermal plants can be built without an underground reservoir; however, there are concerns that this may increase the risk of earthquakes in already geologically active areas. As the world looks for ways to become more environmentally friendly, many different sectors are turning to renewable energy sources. Here at Vision Mechatronics, we are pleased to lower your carbon footprint and save money. Together, we can meet the challenges of climate change by generating renewable energy and supporting clean air policies. We're collaborating to create energy efficient solutions. The future depends on the sustainable work we do today.